If the word “rewilding” makes you think of Jurassic Park, you’re not entirely off track, but not quite there either. While this approach doesn’t aim to revive extinct species, it plays a crucial role in bringing endangered animals back to their natural habitats. But it’s not ending there.
Rewilding: definition
Rewilding is a conservation approach to ecological restoration that enables natural processes to restore and shape ecosystems with minimal human intervention. Oftentimes, it involves reintroducing key species and regenerating habitats to improve biodiversity and ecosystem health. By minimizing anthropogenic action, rewilding promotes ecosystems that regulate themselves, allowing nature to take over. The aim is to create balanced and resilient ecosystems that flourish without constant human intervention.

Rewilding projects: how it works in real life
Rewilding initiatives share a common goal of restoring natural balance, though they can take very different forms. Certain projects prioritize reintroducing essential animal species to help regulate ecosystems naturally. Others focus on connecting fragmented landscapes to enable wildlife to roam and enhance genetic diversity (wildlife corridors). In some cases, the simple act of non-intervention, allowing nature to heal independently, can produce remarkable outcomes. Each project is specifically designed to address the unique needs of its local environment.
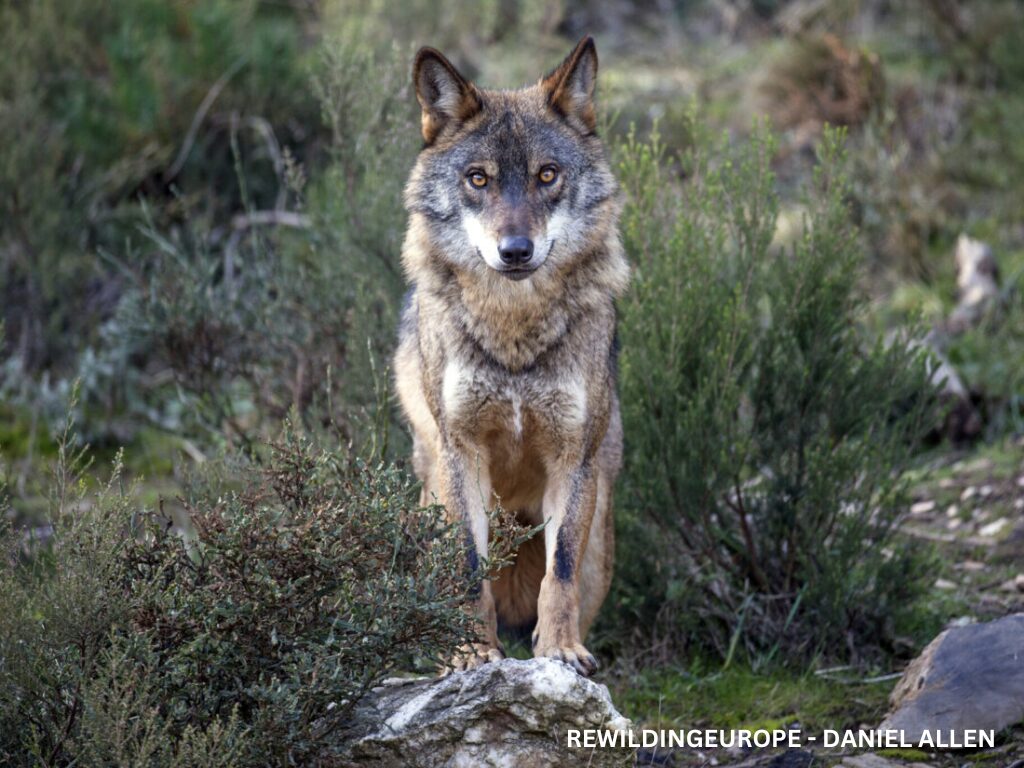

Benefits of rewilding
Rewilding offers numerous benefits to our planet. By restoring damaged ecosystems and allowing natural processes to resume, it revives biodiversity, helping to build resilience against climate change. Stabilization of the soil, reduction of swell effects on the coast, flood protection, mitigation of wildfire, are some of the possible impacts of reforestation. Rewilding creates self-regulating landscapes that are both cost-effective and sustainable.

Stakes of rewilding
Despite its positive outcomes, rewilding presents challenges requiring thoughtful management. Human-wildlife conflict poses a primary obstacle, especially when large predators return to landscapes. Community engagement through comprehensive consultation processes and education are fundamental to lasting success. Also, legal frameworks are necessary to safeguard reintroduced species and their habitat from exploitation or destruction (hunting, timbering…). The most successful results come from all the stakeholders: authorities, conservation organizations and local communities working in concert.

Rewilding examples on explorer.land
Many inspiring projects can be explored on explorer.land. These initiatives demonstrate the power of rewilding in action, whether restoring degraded landscapes or reintroducing species that play a crucial role in their ecosystems.
Find out about the different rewilding projects featured on explorer.land: https://explorer.land/x/projects
And among them, discover the many projects of:
– Global Rewilding Alliance: https://explorer.land/x/organization/gra
– Rewilding Europe: https://explorer.land/x/organization/rewilding-europe
For insights into the importance of tracking and visualizing global rewilding efforts, read our article “Why Map the World’s Rewilding Efforts?”: https://blog.explorer.land/2022/04/25/why-map-the-worlds-rewilding-efforts/
See the projects in action!

Complementary resources about rewilding:
- Rewilding Principles by The Rewilding Thematic Group leaded by @CEM and the @IUCN: https://iucn.org/sites/default/files/2022-10/principles_of_rewilding_cem_rtg.pdf
- The benefits and risks of rewilding: https://iucn.org/sites/default/files/2022-04/rewilding_issues_brief_final.pdf