Environmental projects play a critical role in protecting and restoring our planet. From reforestation and biodiversity conservation to sustainable agriculture and clean energy initiatives, these projects contribute to a healthier environment and a more sustainable future. However, securing funding for environmental initiatives remains a significant challenge, especially with the multitude of funding sources available.
In this guide, we break down the different types of funding opportunities available for environmental projects, providing key insights into each option’s benefits, expectations, and processes. Whether you’re an NGO, start-up, or community group, understanding these pathways can help you access the resources needed to bring your vision to life.
Table of Contents
1. Grants

Grants are one of the most sought-after funding sources for environmental projects. Offered by governments, foundations, and non-profit organizations, grants are non-repayable funds designed to support initiatives with significant social or environmental benefits. For early-stage or non-profit projects, grants are often the most accessible funding option.
How It Works: Grant providers require applicants to meet specific eligibility criteria and submit detailed proposals. These proposals typically outline the project’s goals, expected impact, and budget.
Examples of Grant Programs:
- The National Fish and Wildlife Foundation (NFWF): Provides funding for conservation initiatives that protect wildlife habitats in the United States. Learn more
- The EU’s LIFE Programme: Supports nature conservation, climate action, and environmental protection projects across Europe. Learn more
- Green Climate Fund (GCF): Offers large-scale funding for climate adaptation and mitigation projects globally. Learn more
- Conservation, Food, and Health Foundation: Provides grants for projects focused on ecosystem conservation, agriculture, and public health. Learn more
- Global Environment Facility (GEF): Supports environmental initiatives addressing biodiversity, climate change, and land degradation. Learn more
✅ Pros: Grants do not require repayment and are widely available for environmental projects with strong social outcomes.
❌ Cons: Grant applications are highly competitive, and recipients must meet reporting and compliance requirements.
Pro Tip: Looking to streamline your grant search? Visit explorer.land’s Funding Opportunities to discover tailored opportunities for nature-based solutions.
2. Impact Investments
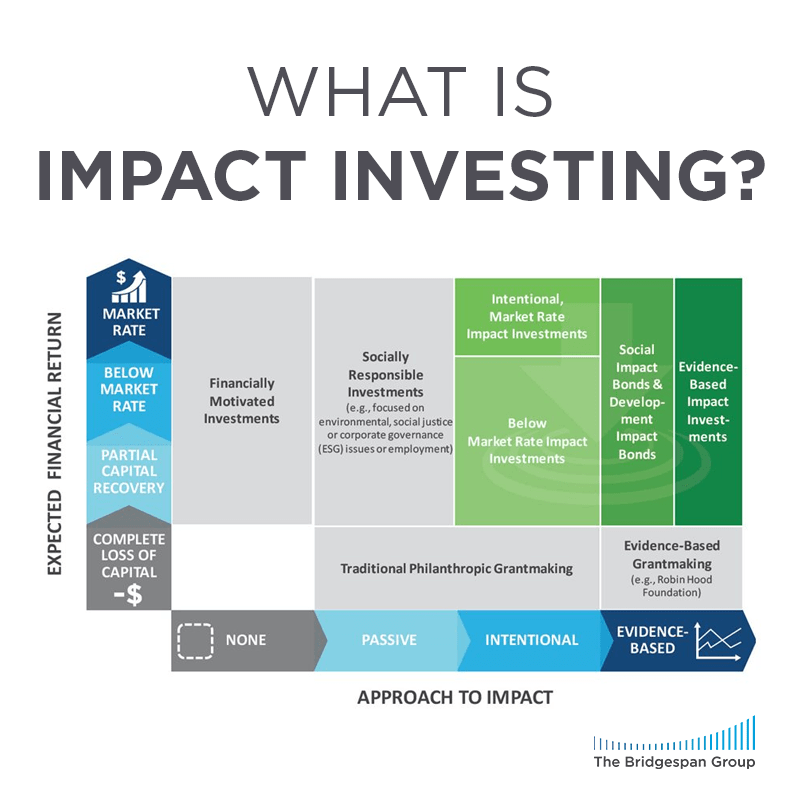
Impact investments combine financial returns with measurable social and environmental outcomes. This funding option is ideal for revenue-generating environmental projects like renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, or carbon offset initiatives.
How It Works: Impact investors provide capital in exchange for equity or debt. They expect financial returns while ensuring the project aligns with their sustainability goals.
Examples of Impact Investment Firms:
- Generation Investment Management: Funds sustainable businesses combating climate change. Learn more
- The Nature Conservancy’s NatureVest: Mobilizes private capital for conservation and eco-tourism projects. Learn more
- Acumen: Provides patient capital to enterprises addressing social and environmental challenges. Learn more
- Triodos Investment Management: Invests in projects focused on renewable energy and biodiversity protection. Learn more
- Blue Earth Capital: Focuses on investments in environmental sustainability and climate resilience. Learn more
✅ Pros: Impact investments provide scalable capital and often include mentorship and network support.
❌ Cons: Projects must generate revenue and may require profit-sharing or investor influence.
Explore 7 Essential Tips to Attract Nature Investors to refine your strategy for securing impact investments.
3. Crowdfunding

Crowdfunding empowers organizations to raise funds from a community of supporters through online platforms. It’s especially effective for grassroots projects that emphasize community involvement and impact.
How It Works: Environmental organizations create campaigns on crowdfunding platforms, detailing their goals and funding needs. Supporters contribute small amounts, often receiving updates or rewards in return.
Exhaustive List of Crowdfunding Platforms:
- GoFundMe: A global platform for direct fundraising. Learn more
- Patreon: Supports creators and organizations through ongoing funding. Learn more
- Kickstarter: Crowdfunds creative and innovative projects. Learn more
- Chuffed: Specializes in non-profit and environmental fundraising. Learn more
- Indiegogo: Enables global fundraising for creative and impact-driven projects. Learn more
- Localgiving: Focuses on supporting small charities and community groups through local crowdfunding campaigns. Learn more
- GlobalGiving: Connects donors with grassroots projects around the world, providing funding to impactful initiatives. Learn more
- DonateFlow: Provides simple, customizable fundraising tools for non-profits and charities. Learn more
- The Big Give: Doubles donations during specific campaigns to maximize fundraising for charities and non-profits.Learn more
- Donr: Mobile-first platform for donations, allowing charities to collect funds through text and online campaigns. Learn more
- TotalGiving: Provides tools for charities to collect and manage online donations. Learn more
- The Good Exchange: Matches projects with funders and enables seamless donations. Learn more
- Crowdfunder: A platform to raise funds for projects, businesses, and causes through community support. Learn more
- JustGiving: One of the largest platforms for personal, charity, and crowdfunding projects. Learn more
✅ Pros: Crowdfunding connects projects to a global audience and fosters community support.
❌ Cons: Campaign success relies on strong marketing and storytelling, which can be time-consuming.
4. Corporate Sponsorships and Partnerships

Corporate sponsorships allow businesses to support environmental projects while enhancing their social responsibility profiles. These partnerships are mutually beneficial, offering companies positive brand visibility and projects access to critical resources.
How It Works: Organizations propose partnership opportunities to corporations aligned with their mission. In exchange for funding, companies often seek recognition, media coverage, or employee involvement in the project.
Exhaustive List of Corporate Initiatives:
- 1% for the Planet: Businesses donate 1% of annual sales to environmental causes. Learn more
- Salesforce Sustainability Cloud Grants: Supports technology-enabled climate solutions. Learn more
✅ Pros: Corporate partnerships provide substantial funding and access to expertise.
❌ Cons: These agreements may include brand deliverables and obligations that could impact project autonomy.
5. Government Loans and Incentives

Governments play a vital role in financing environmental projects by offering low-interest loans, rebates, and tax incentives for sustainability initiatives.
How It Works: Eligible projects can apply for loans with favorable repayment terms or benefit from tax credits that reduce costs for activities like renewable energy adoption.
Examples:
- U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA): Supports renewable energy and conservation projects in rural communities. Learn more
- European Investment Bank (EIB): Offers financing for green projects focused on sustainability across Europe. Learn more
- Canada Green Jobs Initiative: Provides funding for youth-led environmental projects. Learn more
✅ Pros: Low-cost financing and incentives can accelerate project implementation.
❌ Cons: Loan-based funding requires repayment, and eligibility criteria may be strict.
6. Carbon Credit Sales

Projects that reduce carbon emissions, such as reforestation or clean energy initiatives, can generate carbon credits and sell them to organizations seeking to offset their carbon footprints.
How It Works: Projects measure and verify their carbon reduction, then sell credits on the carbon market.
Examples of Carbon Credit Platforms:
- Verra: Certifies carbon credits under the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS). Learn more
- Gold Standard: Recognizes high-quality credits that deliver both environmental and social benefits. Learn more
- Plan Vivo: Supports community-based carbon initiatives.
✅ Pros: Carbon credits generate recurring revenue and align with global climate goals.
❌ Cons: Certification processes can be complex, and market demand may fluctuate.
For a deeper understanding of nature investment trends, check out Top 5 Trends in Nature Investments.
7. Philanthropic Funds for Nature-Based Solutions

Philanthropic funds are typically managed by foundations, donor networks, or organizations focused on global environmental sustainability. These funds operate by providing financial support to projects that align with their mission to protect, restore, and sustainably manage ecosystems. Unlike investments, philanthropic funds do not expect financial returns, but they may require impact reporting and measurable outcomes to ensure funds are effectively utilized.
Examples:
- The Bezos Earth Fund: A platform specifically supporting nature-based solutions, climate initiatives, and environmental restoration projects. Learn more
- Conservation International: Funds projects that protect biodiversity, forests, and marine ecosystems through philanthropic partnerships. Learn more
- Rainforest Trust: Provides funding for projects dedicated to protecting rainforests and critical habitats worldwide. Learn more
- Wildlife Conservation Network (WCN): Facilitates donations to grassroots projects supporting endangered species and ecosystems. Learn more
- Re:wild Action funds: Supports innovative and scalable NbS projects that address biodiversity loss and ecosystem degradation. Learn more
✅ Pros: Donations require no repayment and allow for flexible project implementation.
❌ Cons: Consistent outreach is needed to sustain donor support over time.
Conclusion
Securing funding for environmental projects requires a strategic approach. By understanding the diverse options—grants, impact investments, crowdfunding, carbon credits, and more—organizations can create a sustainable funding model to drive impactful change.
To connect your project with funders passionate about nature-based solutions, explore explorer.land. By showcasing your project on this innovative platform, you can attract funding partners who share your commitment to a greener, healthier planet.


